Communication is part of human nature and the need for faster communication has resulted in the development of different methods such as mailing, printing, phones, mobiles, computers, and the internet, which have all changed the course of human history. Advances in communication have always allowed the evolution of cultures. Nowadays, Social Media (SoMe) is changing the way people live, communicate, and interact globally. The applications of SoMe in healthcare and its role in scientific communication represents a growing area of interest that is providing great opportunities in the urological community. In our study we aimed to assess the influence of SoMe on urological knowledge acquisition among young urologists across Europe.
The European Society of Residents in Urology, German Society of Residents in Urology, and the Spanish Residents and Young Urologists Workgroup members designed a 20-item online survey. The survey was distributed via email in 23 European countries to urology residents and young urologists. Survey design and distribution was performed in concordance with the CHERRIES (Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys) guidelines. SPSS (IBM, New York, USA) was used for statistical calculations comparing the use of SoMe in urologists in two age groups with a cut-off of 35 years of age.
Three hundred and sixteen residents and young urologists with a mean age of 31.2±3.9 years responded to the survey; of these residents, 79% were in training with a mean of 4.1±3.0 years of training, and 21% were certified urologists. SoMe was used by 99% of respondents in personal and professional capacities. Facebook was the most frequently used platform for personal use whilst YouTube and LinkedIn were used most frequently for professional use (Figure 1). A total of 44% of the respondents had an academic or professional profile on a SoMe platform. SoMe was ranked in third place as an information source for urological news and updates behind journals and websites, and ahead of congresses and books. Video content from YouTube or other sources was ranked as the preferred tool to see/understand surgical techniques ahead of websites and reference books. Sixty-one percent of respondents followed urological associations, 47% followed urological events, 44% followed urological journals, and 39% followed urological experts on SoMe. The influence of SoMe on urology knowledge was rated as moderate-to-high by 63% of young urologists and as low-to-none by 37%. The application of guidelines on the appropriate use of SoMe in urology was observed in 44%. Comparative analysis of respondents’ SoMe use revealed that certified urologists rated the influence of SoMe on their urology knowledge as higher (p=0.036) and applied SoMe guidelines more frequently (p=0.008) than urology residents.
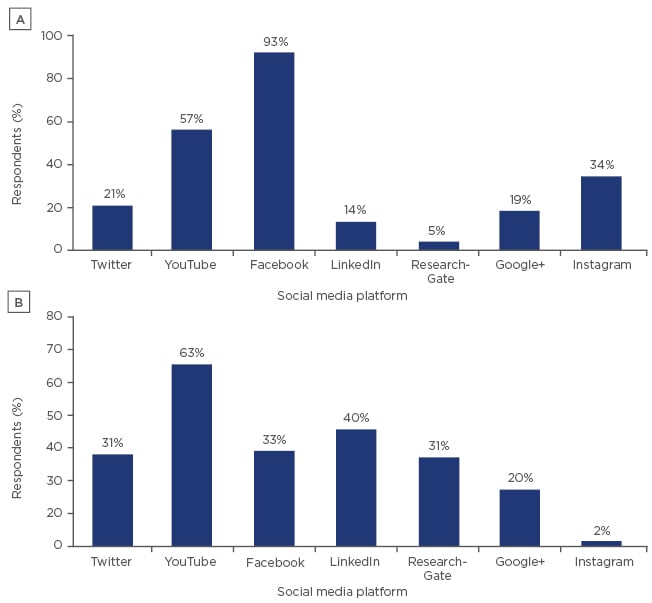
Figure 1: Usage rates of social media platforms for personal A) and professional B) purposes.
With these findings we may conclude that SoMe plays a significant role in the knowledge acquisition of young urologists in Europe. SoMe represents a vibrant arena of opportunities for the communication of knowledge in healthcare, and their potential application today is unquestionable. At present the benefits include communication between associations, urologists, residents, other healthcare professionals, and patients. SoMe facilitates networking and dissemination of studies’ results, as well as extensive experience of events, conferences, and meetings. Physicians, organisations, and institutions should strive to spread and provide valuable educational content through SoMe.