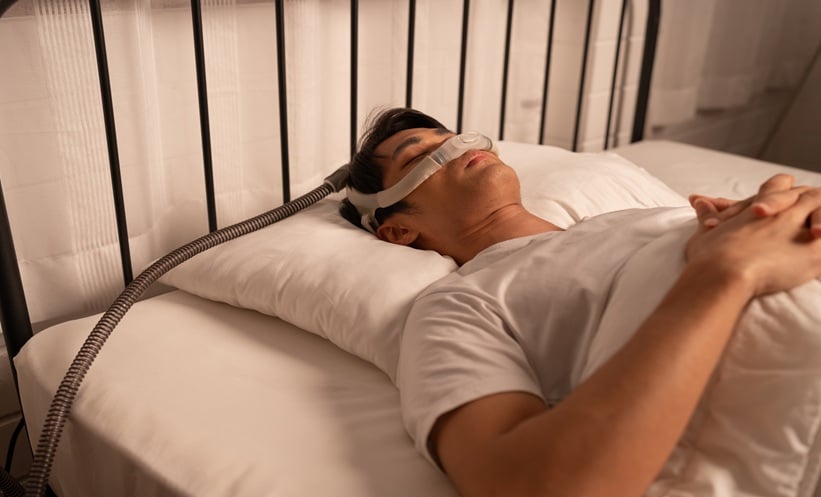
A SYSTEMATIC review and meta-analysis has confirmed that positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy significantly reduces the risk of both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The study, which analyzed data from over 1.17 million individuals, underscores the critical role of PAP therapy in improving survival rates for OSA patients.
Researchers reviewed 30 studies, including ten randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 20 non-randomized controlled studies (NRCSs), covering a diverse population with a mean age of 59.5 years. The findings revealed that PAP therapy was associated with a 37% reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.56–0.72; p<0.0001). More strikingly, cardiovascular mortality risk was nearly halved in PAP users compared to non-users (HR 0.45, 95% CI 0.29–0.72; p<0.0001). The study also found that the life-extending benefits of PAP therapy increased with consistent use. Obstructive sleep apnea, a condition characterized by repeated airway obstruction during sleep, is a known contributor to cardiovascular disease and premature death. Despite the well-documented benefits of PAP therapy, patient adherence remains a challenge. This latest research highlights the therapy’s substantial impact on survival, reinforcing the need for improved patient education and support to enhance compliance. Clinicians should actively discuss these findings with patients with OSA, emphasizing that PAP therapy is not just about improving sleep quality but also about significantly extending life expectancy. With a growing body of evidence supporting its effectiveness, PAP therapy remains a cornerstone treatment for managing OSA and its associated health risks. Reference: Benjafield AV et al. Positive airway pressure therapy and all‐cause and cardiovascular mortality in people with obstructive sleep apnoea: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and confounder-adjusted, non-randomised controlled studies. Lancet Respir Med. 2025. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(25)00002-5. Anaya Malik | AMJ