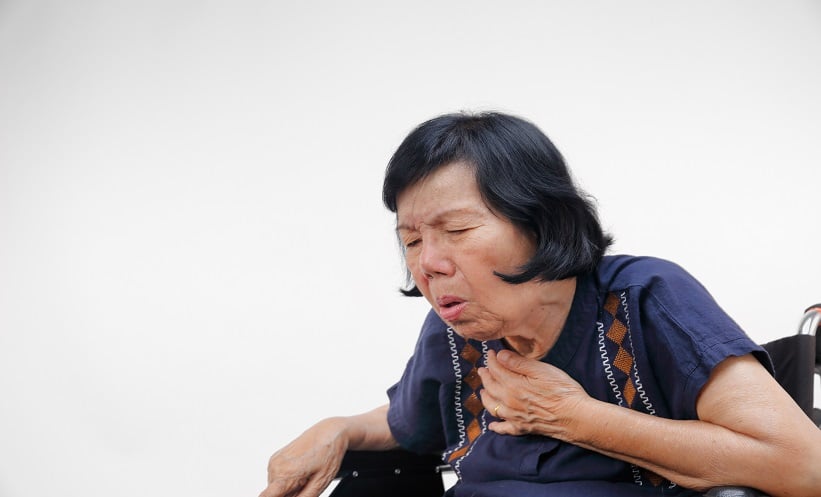
A NEW study has shown that the BACES score, a clinical tool used to predict mortality in non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) lung disease, can also help predict treatment outcomes in patients with Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease (MAC-LD). This research was presented at the CHEST Annual Meeting 2024 in Boston, October 6-9, evaluating the score’s application in the U.S. clinical setting.
The BACES score incorporates BMI <18.5 kg/m², Age ≥65, Cavity presence, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and male Sex. In a retrospective analysis the study analyzed 123 patients with MAC-LD comparing treatment outcomes based on BACES scores. Patients were divided into two groups: those receiving antibiotics and those managed through airway clearance without antibiotics. The median patient age was 68.8 years, and BMI averaged 22.5 kg/m². Notably, patients with a BACES score of 0 were significantly younger than those in higher score groups. Differences in treatment outcomes were observed among BACES scores 0, 1, 2, and 3, with clinical improvement rates of 94.3%, 96.4%, 85.2%, and 50%, respectively. Overall clinical-radiological improvement-stability response rates were 94.3%, 96.4%, 84.6%, and 50%, respectively. However, worsening radiological response rates by BACES scores were 8.8%, 14.8%, 17.4%, and 50%, respectively, but did not reach statistical significance. Sputum culture persistence did not change significantly by BACES scores and remained similar across the groups. The BACES score shows promise as a tool for predicting clinical and radiological responses in patients with MAC-LD; however, it was not associated with culture conversion and radiological worsening over time. For healthcare professionals, the BACES score can be considered as a predictor of clinical and radiological response but not microbiological response associated with treatment outcomes. The study authors suggest prospective studies would be needed to determine the predictive value of this clinical score and other factors to guide treatment decisions. Reference: Reddy Vadiyala M. Treatment outcomes and baces score in patients with mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. CHEST. 2024:166(4):A1628-A1629. Anaya Malik | AMJ