PURPOSE
Incidental pulmonary embolisms (IPE) on CT are missed in up to 70% of cases. While AI tools for IPE detection exist, an evaluation on if and how these tools can provide actual value, e.g., fit patients and end-users’ needs (i.e., radiologists), has never been performed.1 The aim of this early health technology assessment is to determine the requirements for a value-based AI tool for IPE detection on CT.
METHODS
A comprehensive early assessment of radiology-AI was proposed and conducted for IPE. A literature search, structured interviews, focus groups, and evaluation meetings were performed with the identified stakeholders to define criteria and scenarios for a multiple criteria decision analysis. A representative survey was developed and circulated to weigh the importance of the criteria and assess the performances of four possible AI designs. Multiple criteria decision analysis on the survey helps quantify the value requirements.
RESULTS
Consultations with radiologists, treating physicians, patients, radiology technologists, AI specialists, legal experts, and ethicists resulted in 14 sub-criteria and five main criteria: patient impact, model performance, physician support, environmental impact, and costs (Figure 1). Preliminary outcomes indicate that although patient impact due to missed or delayed diagnosis is deemed the most important criterion, increasing the model performance and extending the physician support meaningfully improves the value of the AI tool.
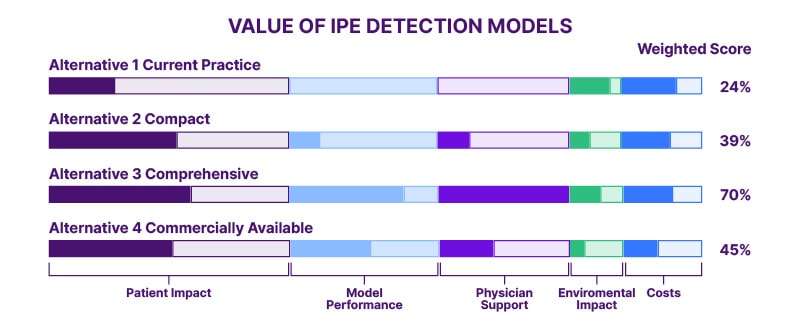
Figure 1: Four evaluated alternative AI model design proposals for detection of incidental pulmonary embolisms.
The five main criteria, based on the expert elicitation, have been defined as patient impact, model performance, physician support, environmental impact, and costs. Their relative importance is depicted by the lengths of each of the bars. The potential performance of the alternative for each criterion is shown by the bar infill, where a longer infill means a higher score. The weighted average for each alternative is provided.
IPE: incidental pulmonary embolism.
CONCLUSION
Development of impactful AI, which improves patient outcomes meaningfully and meets the needs of end-users, requires a broad assessment before development. Early health technology assessment is a structured method that provides insight on what will be impactful.