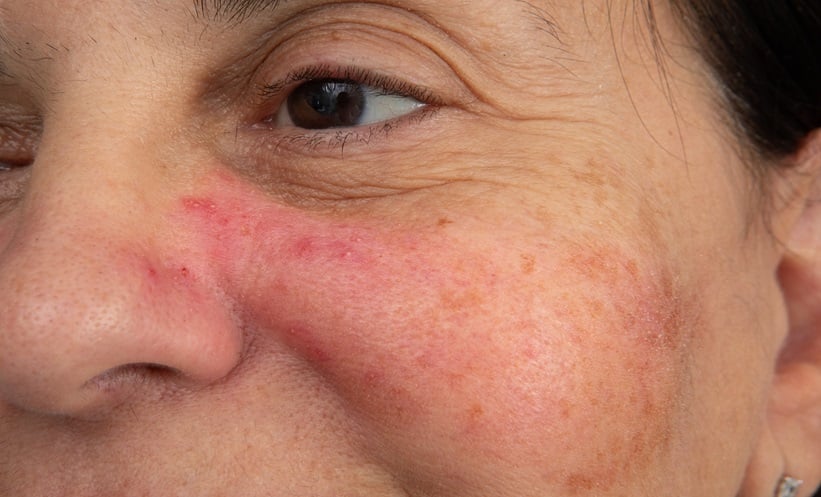
ROSAECEA, a chronic inflammatory skin disease, is characterised by erythema, pustules, papules, and flushing. Effective treatment repairs the skin barrier and in doing so reduces inflammation and promotes vasoconstriction. New research finds that topical ferulic acid significantly improves skin lesions and barrier function in patients with papulopustular rosacea, with minimal side effects. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of ferulic acid in managing rosacea symptoms and improving skin barrier function.
In total, 60 patients with mild to moderate rosacea were randomised into an observation group treated with ferulic acid and a control group using saline, with both groups also taking doxycycline.
Results showed that after six weeks, both groups had improvements in skin lesion assessments and self-reported scores, but the observation group experienced significantly greater progress. This group also saw an 80% effective rate compared to 63.33% in the control group, with VISIA imaging results corroborating these findings. Reported side effects in the ferulic acid group were minor, including a greasy sensation and mild tingling in a few patients.
These results support the potential of ferulic acid as an adjuvant therapy for rosacea, improving both lesions and skin resilience. This has clinical relevance as ferulic acid may offer a less invasive, tolerable option for rosacea management, addressing skin inflammation and barrier restoration without severe side effects, and could be incorporated into rosacea treatment guidelines as a topical therapeutic option. Future research should further investigate long-term effects, optimise treatment protocols, and explore the combined impact with other therapies to refine and enhance clinical outcomes.
Reference
Wang X et al. Ferulic Acid in the Treatment of Papulopustular Rosacea: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024. DOI:10.1111/jocd.16611.