Advances in the understanding of prostate cancer (PCa) biology have led to the development of several new agents targeting different aspects of the malignant process which have been shown to prolong life. Clinical factors such as prostate- specific antigen (PSA) and pathological factors such as Gleason grading and tumour, node, and metastasis (TNM) staging are well known as prognostic markers in PCa. These tools are often insufficient for an accurate risk stratification of each patient. Therefore, it is essential for therapy monitoring to provide qualified surrogate biomarkers for survival, the ability to characterise the changing biology of the tumour at the patient’s level, and qualified predictive biomarkers that can guide treatment selection based profiles derived from individual characterisation. Therefore, the detection of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in the blood of patients with PCa might, in addition to their prognostic value, serve as liquid biopsy complementing or replacing PSA determination in predicting and monitoring the response to different therapies.1
We present data from a pilot study comparing different biomarkers. The CTCs represent the in vivo biomarker which were isolated by the CellCollector® (GILUPI, Potsdam, Germany) from the peripheral venous blood. The multiplex assay was used for the determination of the ex vivo biomarkers: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, leptin, urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), and uPA receptor (uPAR) were measured in serum samples.
We enrolled 34 PCa patients, 21 with localised (PCa-l) and 13 with metastasised prostate cancer (PCa-m). At multiple periods throughout the treatment, CTCs and a Luminex® assay were determined. The CellCollector was inserted in a cubital vein for 30 minutes. The interaction of target CTCs with the CellCollector was mediated by an antibody to the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). Captured CTCs were identified based on histological
cell architecture by immunofluorescence staining using cytokeratin (8, 18, 19), positive nuclear Hoechst staining, as well as CD45 negative staining as criteria to exclude EpCAM positive leukocytes. The Luminex assay is a bead-based principle which requires a small sample volume (≤50 µL) for the determination. All analytes could be simultaneously detected.
The baseline characteristics such as BMI, age, and smoking status were similar in all patients. The number of in vivo captured CTC in PCa-m patients varied from 0–820, with a mean of 17.9 CTCs and a median of 5, and in PCa-l patients the number ranged from 0–8 CTCs, with a mean of 1.6 CTCs and median of 0 was reported (Figure 1a). The CTC count, the PSA level, and the Gleason grading were significantly different in our two groups. The leptin level showed a significant difference between the two groups. In the levels of HER-2, IL-6, IL-8, uPA, and uPAR no significant differences appeared. Interestingly, significant correlations between PSA and uPAR r=0.401**; HER-2 r=0.523**; IL-8 r=0.49***; uPA r=0.324**; leptin r=-0.286**; IL-6 r=-0.298** in PCa-m patients were demonstrated. Unfortunately, the CTC numbers showed no correlation between the ex vivo biomarkers. The overall survival for metastasised patients with <5 CTCs was significantly (p<0.031) better than for patients with ≥5 CTCs (Figure 1b). Some personalised marker profiles of the patients displayed a correlation between the ex vivo and in vivo biomarkers (Figure 2)
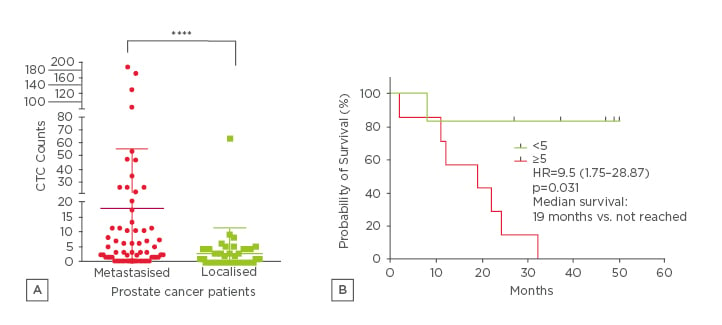
Figure 1:
A) CTC enumerations in 35 PCa patients evaluated with the CellCollector. Results of CTC enumerations of PCa-m patients (mean of 17.9 CTCs during therapy) and PCa-l mean of 1.6 CTCs (0-8 CTC), (data show the mean and interquartile range). B) Kaplan–Meier demonstrated a significant (p<0.031) better OS for patients with <5 CTCs.
PCa: prostate cancer, CTC: circulating tumour cells, HR: hazard ratio; PCa-m: metastasised prostate
cancer; OS: overall survival.
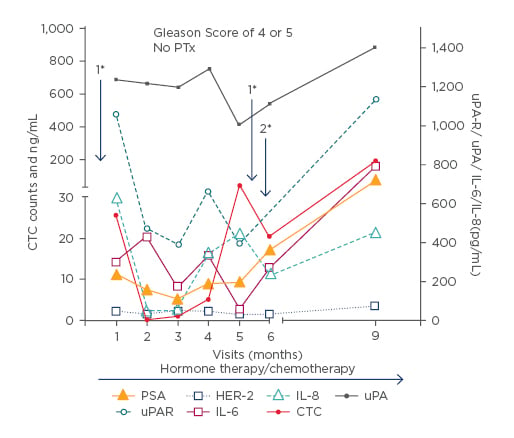
Figure 2: Individual patient sample:
Only 6 days after study inclusion and after 5 months a palliative TURP (*1) was performed beside a
continuous hormone therapy and radiotherapy and removal of a brain metastasis between months 5 and 6 (*2).
PSA: prostate specific antigen; HER-2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IL: interleukin; uPA:urokinase plasminogen activator; uPAR: uPA receptor; CTC: circulating tumour cells; PTx: primary tumour cannot be assessed; TURP: transurethral resection of the prostate.
The in vivo captured CTCs appeared to be a useful prognostic marker because the survival rate of patients with <5 CTCs was significantly better. These results confirmed the prognostic and predictive value of overall survival.2,3 However, it is important that issues related to sensitivity and enumeration without functional characterisation of the captured cells may limit the generalisability of the assay.4 Although there was no general validity, single patient analyses showed several, partly significant correlations between CTC count, PSA level, and ex vivo parameters; therefore, these markers could be useful in individual risk stratification and therapeutic decision-making.