Fractalkine (CX3CL1, designated as FKN hereafter) is the sole member of the CX3C chemokine family which leads to dual actions, chemotaxis, and cell adhesion for leukocytes expressing the cognate receptor CX3CR1. The authors have conducted clinical trials of E6011, a novel humanised anti-FKN monoclonal antibody, for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Japan.1 This is the first report of results of efficacy and safety for E6011 from a Phase II, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group comparison study in RA patients inadequately responding to methotrexate (MTX-IR).2
During the 24-week double-blind period, 190 patients in total with moderate-to-severe active RA of MTX-IR were randomly assigned to E6011 (100 mg: n=28, 200 mg: n=54, and 400/200 mg: n=54) or placebo (n=54) at a 1:2:2:2 ratio. In the E6011 100 mg, 200 mg, and placebo groups, subjects received E6011 at Weeks 0, 1, 2, respectively, and every 2 weeks subsequently. In the E6011 400/200 mg group, subjects received 400 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and then 200 mg every 2 weeks subsequently.
The ACR20 response rate at Week 12 (non-responder imputation), the primary endpoint, was not statistically significant (Placebo: 37.0%, 100 mg: 39.3%, 200 mg: 48.1%, and 400/200 mg: 46.3%). However, statistically significant difference from placebo in ACR20 response rate was found in the 200 mg and 400/200 mg groups at Week 24 (Placebo: 35.2%, 100 mg: 39.3%, 200 mg: 53.7%, and 400/200 mg: 57.4%). In addition, the authors focussed on CD16+ monocytes which highly expressed FKN receptor/CX3CR1 as a blood biomarker and are linked to the clinical response to E6011. Exploratory, the whole patient population was divided into 2 groups according to the median value of baseline CD16+ monocyte percentage (median: 10.35%). Much clearer ACR20 responses were observed in a dose dependent manner in the subjects who showed higher baseline CD16+ monocytes over the median at Week 24 (NRI) (Placebo: 30.0%, 100 mg: 46.7%, 200 mg: 57.7%, and 400/200 mg: 69.6%), although such fashion was obscure in the subjects below the median value. Adverse events that occurred in ≥5% of subjects in any E6011 group were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, stomatitis, bronchitis, back pain, pharyngitis, and dental caries. E6011 was well tolerated with no notable safety concerns at doses of 100, 200, and 400/200 mg when administered subcutaneously for 24 weeks.
In conclusion, E6011 provided clinical improvements with a good safety profile in RA patients with MTX-IR (Figure 1). Notably, a higher efficacy of E6011 was suggested in patients with higher baseline CD16+ monocytes (%). This is novel evidence suggesting that this new approach to targeting FKN/CX3CR1 interaction could be beneficial for RA.
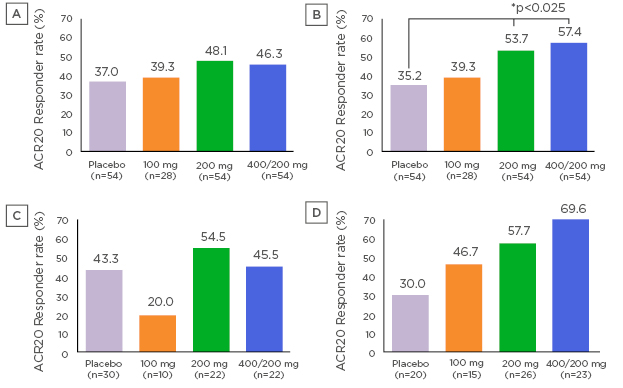
Figure 1: ACR Response rate at Week 12 (A), Week 24 (B) (NRI), Week 24 in MTX-IR RA patients with lower (C) and higher (D) baseline CD16+ monocytes (NRI)
ACR20 response rate at Week 12 was higher in the 200 mg group and 400/200 mg group than the placebo group. However, a statistically significant difference from placebo was not found. ACR20 response rate at Week 24 was statistically significantly higher in the 200 mg group and 400/200 mg group than the placebo group (p=0.023 for the 200 mg group, p=0.01 for the 400/200 mg group; a logistic regression model with Hochberg method). ACR20 response rate at Week 24 in subjects with low baseline CD16+ monocytes (<10.35%) were 43.3% (13/30 subjects) in the placebo group, 20.0% (2/10 subjects) in the 100 mg group, 54.5% (12/22 subjects) in the 200 mg group, and 45.5% (10/22 subjects) in the 400/200 mg group, respectively. ACR20 response rate at Week 24 in subjects with high baseline CD16+ monocytes (≥10.35%) were 30.0% (6/20 subjects) in the placebo group, 46.7% (7/15 subjects) in the 100 mg group, 57.7% (15/26 subjects) in the 200 mg group, and 69.6% (16/23 subjects) in the 400/200 mg group, respectively.