BACKGROUND AND AIMS
The aim of the work is the possibility of respecting diagnostic reference levels (DRL) for CT simulations, preserving a good image resolution required for radiotherapy planning activities.1
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The dosimetric indexes of simulation CT scans were examined in comparison to Italian and European standards. Dose length product and CT dose index values of 80 simulation CT scans of different anatomical districts, acquired in the period of October–November 2022, were collected. Dose length product values exceeded, in particular for head and neck, brain, and pelvis CT scans, the reference values (Figure 1). Following the analysis of the causes, CT acquisition parameters, such as scan field of view, display field of view, pitch, and modulation interval, were modified, and new CT protocols were implemented.2
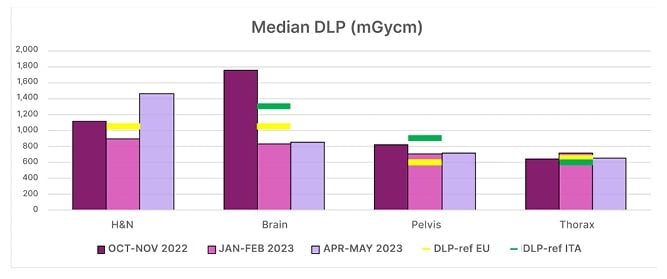
Figure 1: How the average dose length product changed during the periods under review, with reference to EU and ITA regulations.
DLP: dose length product; EU: European Union; H&N: head and neck; ITA: Italy.
An initial evaluation of the results was performed on 80 CT scans acquired in January–February 2023. The changes in CT protocols were then further discussed in terms of dosimetric impact and image quality and resolution. The final observation was performed on 80 scans acquired in April–May 2023, with the final protocols.
RESULTS
During the second analysis, the acquisition parameters were further refined, to optimise the results obtained in quantitative and qualitative terms. For example, for the head and neck district, the previous parameters were restored in favour of a better image resolution, although the DRLs were not respected.3
CONCLUSION
In many cases, it is possible to respect the DRLs alongside clinical/therapeutic requirements, while maintaining good image quality, and reducing the dose delivered to the patient.
LIMITATIONS
CT acquisitions for radiotherapy do not overlap with diagnostic ones, so DRLs are not an absolutely applicable standard. Compliance with these guidelines is, in fact, not mandatory for radiotherapy.