BACKGROUND AND AIMS
Patients on dialysis are characterised by susceptibility to infections, high prevalence of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and poor response to vaccinations,1,2 conditions met mostly in aged individuals. Compromised immune function seen in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is demonstrated by profound immune cell phenotype changes and might be a primary cause for the above-mentioned conditions. These alterations resemble the natural course of senescence, and are, therefore, termed immunosenescence. Whereas alterations of T cells in ESRD have been studied to a certain extent,3 the data concerning the B-cell subpopulation are, to the present, insufficient. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of haemodialysis (HD) on B-cell subsets, in terms of untimely expression of immunosenescent phenotype.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
B-cell phenotype was analysed by flow cytometry in 25 patients with ESRD on HD (15 males and 10 females; mean age: 59±14.7 years). Patients on HD with systemic diseases, malignancy, or a recent (<3 months) episode of infection were excluded. A sample of total blood was collected from the patients before initiation of a mid-week routine dialysis session. A total blood count was performed according to standard methods and a fresh blood sample, with dipotassium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid for anticoagulation, was analysed with flow cytometry. Subpopulations, including naïve (IgD+CD27-), IgM memory (IgD+CD27+), switched memory (IgD-CD27+), and late memory (IgD-CD27-) B cells were determined. Findings were compared to 12 healthy controls of similar age.
RESULTS
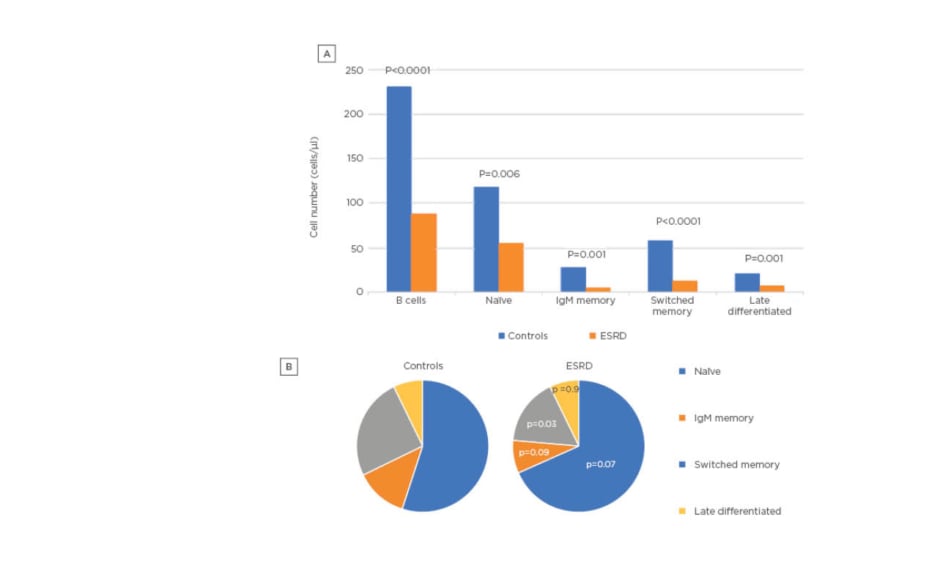
A severe B lymphopenia was observed in patients on dialysis in comparison to healthy controls, affecting both the percentage (6.5±2.7% versus 11.9±4.5%; p<0.0001) and absolute count of B cells (88 [53] versus 229 [271] cells/μL; p<0.0001). A decrease in absolute numbers (Figure 1A) was also seen in all four subsets of B cells (naïve 55 [54] versus 118 [216] cells/μl, p=0.006; IgM memory 5 [11] versus 28 [25] cells/μL, p=0.001; switched memory 13 [10] versus 59 [64] cells/μL, p<0.0001; late memory 7 [7] versus 21 [24] cells/μL, p=0.001). However, whereas naïve, IgM memory, and late memory B cell proportions were similar between patients and controls, switched memory B cell percentage showed a significant decline (Figure 1B) in the dialysis cohort (15.7 [11.7]% versus 25.7 [18.9]%; p=0.03).
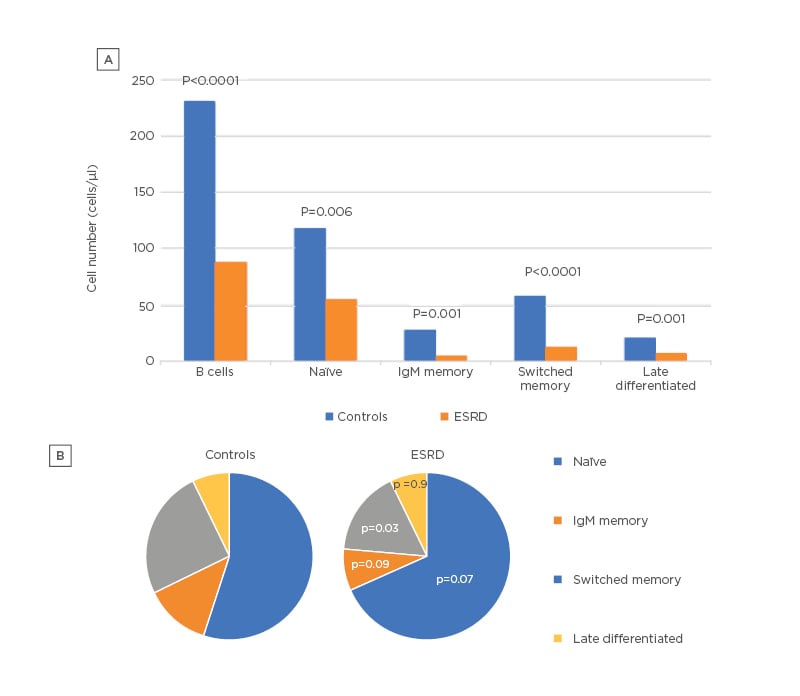
Figure 1: A) B-cell subset counts in healthy controls and ESRD; and B) B-cell subset percentages in healthy controls and ESRD.
ESRD: end-stage renal disease; NS : non-significant.
CONCLUSION
B-cell numbers are known to be severely diminished in healthy aged individuals. A severe decline of switched memory B cells is also observed in normal ageing.4 These latter cells can readily differentiate into plasmablasts after stimulation by the specific antigen and produce a robust humoral response.5 Chronic HD results in B cell lymphopenia and alterations in B-cell phenotype that resemble normal ageing. This may act as an additional factor to relative immune deficiency of patients on dialysis.