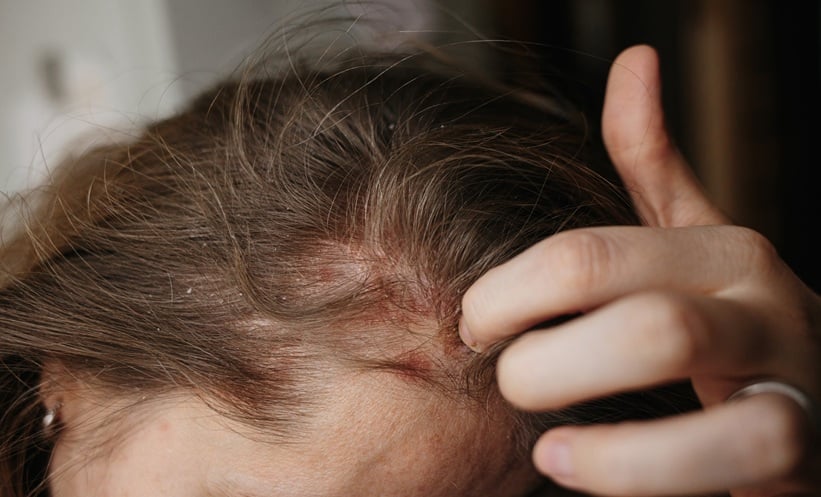
SCALP psoriasis, characterised by erythemato-squamous plaques extending beyond the hairline, remains a challenging dermatological condition. Symptoms such as itching, hair loss, and visible lesions often lead to embarrassment and social stigma. Dermoscopic findings, including regular red dots and white scales, assist in diagnosis and monitoring treatment progress. Despite various available therapies, physical inaccessibility and the refractory nature of scalp psoriasis complicate treatment.
Recent research has investigated the efficacy of excimer light and topical methotrexate (MTX) 1% hydrogel in managing scalp psoriasis. Excimer light, a targeted narrow-band UVB therapy operating at 308 nm, has shown promise by inducing apoptosis in keratinocytes and T lymphocytes. Its anti-pruritic effect likely results from its degenerative impact on cutaneous nerves. While excimer light offers safety and widespread availability, it carries a higher risk of pigmentation compared to excimer laser therapy.
Methotrexate, traditionally a systemic therapy, has been effectively adapted into topical forms, such as 1% hydrogel, for localised plaque psoriasis. This formulation offers anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative benefits without the systemic side effects of oral MTX.
A comparative study assessed the clinical response, safety, and side effects of excimer light and topical MTX 1% hydrogel in treating scalp psoriasis. Results showed significant improvement in Psoriasis Scalp Severity Index (PSSI) scores in both treatment areas, with excimer light showing slightly accelerated results due to higher dose increments. Both therapies significantly reduced itching scores, with mechanisms linked to anti-inflammatory and nerve-related effects.
Patient satisfaction was high for both treatments, though excimer light led to minor side effects such as erythema and hyperpigmentation, while MTX gel caused mild irritation. Dermoscopic findings revealed reductions in red dots and white scales post-treatment. Recurrence rates were low, with excimer light exhibiting a slightly lower recurrence rate compared to MTX gel.
This study highlights the efficacy of excimer light and topical MTX as promising treatments for scalp psoriasis. Larger-scale research with longer follow-ups is necessary to refine these approaches and explore potential combination therapies.
Reference
Moftah NH et al. Excimer light versus topical methotrexate 1% hydrogel in treatment of scalp psoriasis: clinical and dermoscopic study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025;317(1):282.