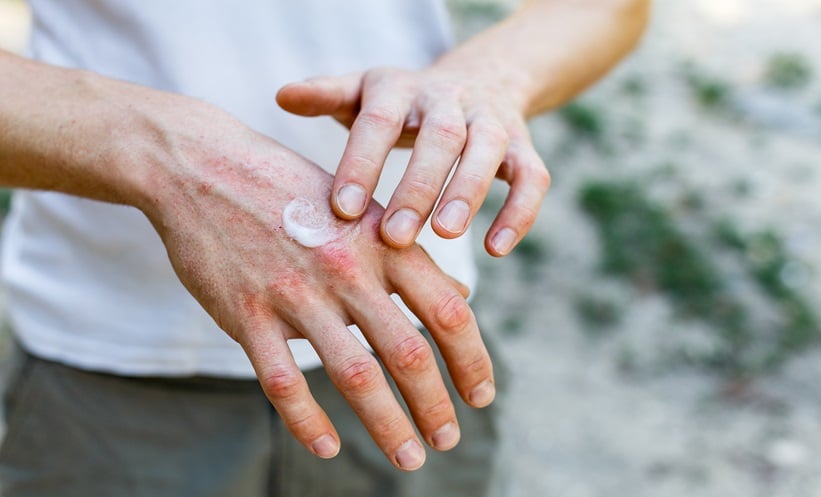
SYSTEMIC inflammation may mediate the link between psoriasis severity and cardiovascular disease (CVD), according to a cohort study involving 769 patients.
This study aimed to investigate the role of systemic inflammation in the relationship between psoriasis skin disease severity and CVD. Using data from two cohorts, the Psoriasis Atherosclerosis and Cardiometabolic Disease Initiative (PACI) and the Stockholm Psoriasis Cohort (SPC), researchers evaluated whether systemic inflammation, measured by GlycA—a glycan biomarker of acute-phase proteins—mediates this relationship. Participants from PACI and SPC included patients with varying psoriasis severity, assessed using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI).
Results revealed that PASI was associated with higher GlycA levels and increased cardiovascular risk. In the PACI cohort, the direct effect of PASI on noncalcified coronary burden (NCB) was estimated at 0.94, with an indirect effect mediated by GlycA at 0.19. In the SPC cohort, the direct odds ratio (OR) of PASI for cardiovascular events was 1.23, while the indirect OR mediated by GlycA was 1.16. Mediation analysis showed that systemic inflammation accounted for 17% of the relationship between PASI and subclinical atherosclerosis and 37% of the relationship between PASI and cardiovascular events, with statistical significance in both cases.
These findings underscore the importance of addressing systemic inflammation in clinical management of psoriasis patients to mitigate cardiovascular risk. GlycA emerges as a potential biomarker to identify high-risk individuals and evaluate treatment effectiveness. Future research should explore targeted interventions that reduce inflammation to prevent CVD in psoriasis patients. Clinicians are encouraged to integrate cardiovascular risk assessments into psoriasis care, with an emphasis on holistic management strategies.
Reference
Svedbom A et al. Skin Inflammation, systemic inflammation, and cardiovascular disease in psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;DOI:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.4433.