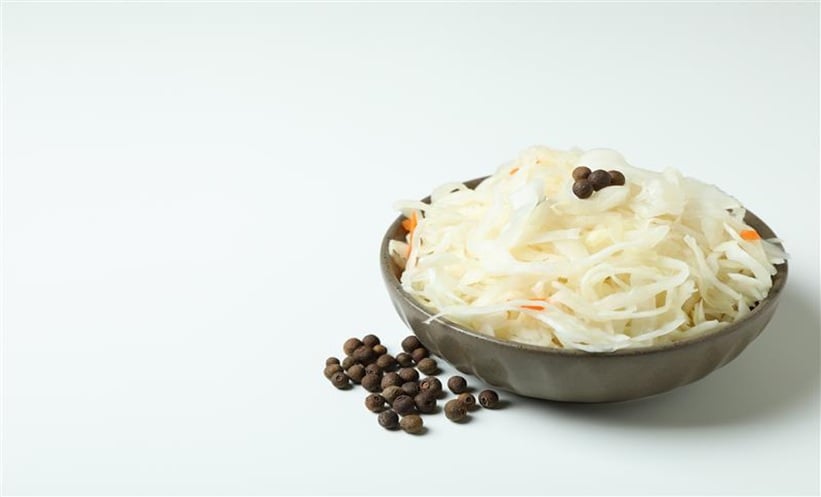
A NEW study sheds light on how fermented cabbage, like sauerkraut, supports gut health by protecting intestinal barrier function from inflammatory stress.
Researchers from the University of California, Davis, investigated how soluble compounds formed during cabbage fermentation impact intestinal epithelial cells when exposed to inflammatory cytokines interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Using Caco-2 monolayers as a model of the intestinal lining, they found that fermented cabbage extracts, but not raw cabbage or brine, significantly preserved barrier integrity.
The study showed that fermentation consistently enriched cabbage with bioactive metabolites, including lactic acid, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and amino acid derivatives such as D-phenyl-lactate and indole-3-lactate. These compounds, alone or in combination, only partially replicated the full protective effect of fermented cabbage, suggesting a synergistic action among multiple metabolites.
Interestingly, the protective benefits were observed across both laboratory-prepared and commercially available ferments, regardless of whether a probiotic strain (Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LP8826R) was added. This indicates that cabbage fermentation naturally produces health-supportive compounds, with minimal dependence on specific fermentation methods.
The findings provide compelling mechanistic evidence supporting the gut-health claims often associated with fermented foods. They also underscore the importance of the full fermented matrix, rather than isolated components, in maintaining intestinal barrier function under inflammatory stress.
Reference
Wei L, Marco ML. The fermented cabbage metabolome and its protection against cytokine-induced intestinal barrier disruption of Caco-2 monolayers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025;DOI: 10.1128/aem.02234-24.